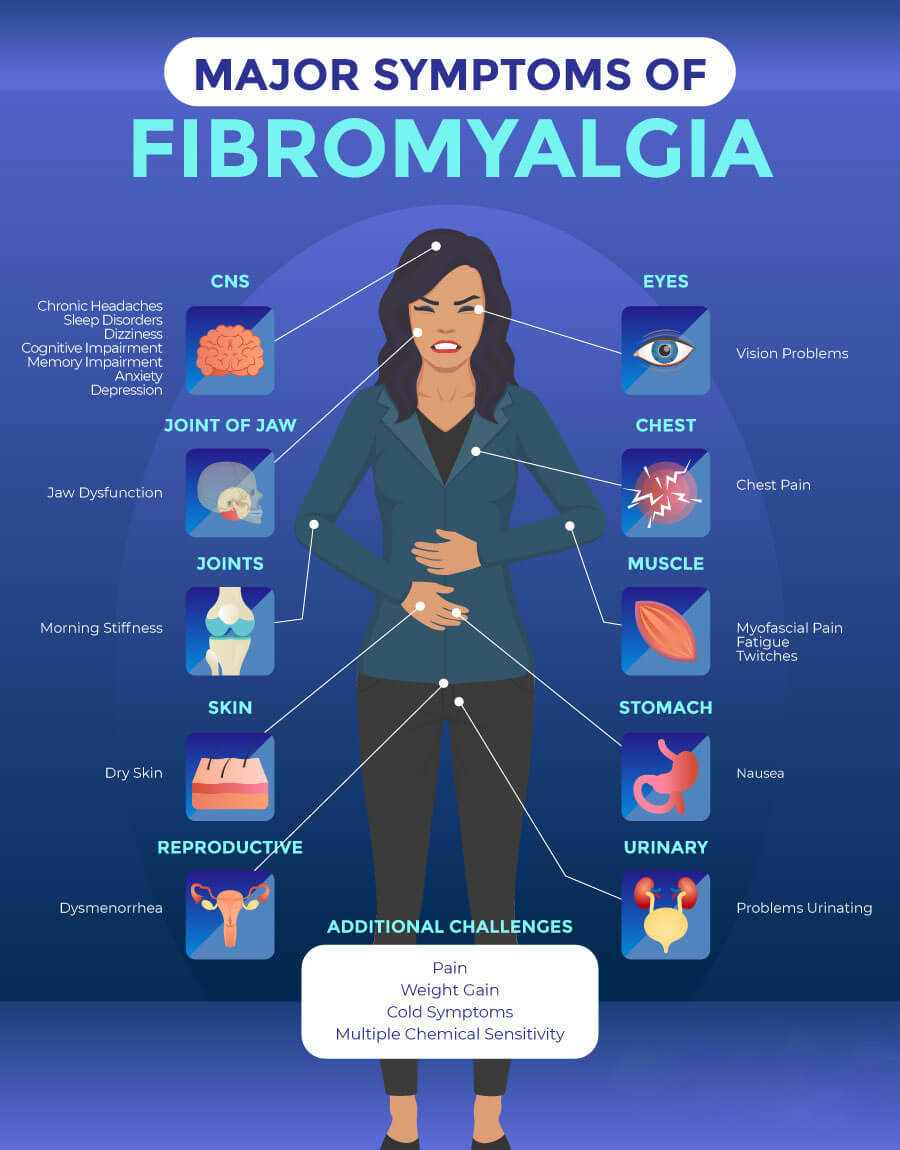
Living with fibromyalgia can be a challenging journey, as individuals grapple with persistent pain, fatigue, and other debilitating symptoms. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, medications play a crucial role in managing fibromyalgia symptoms. In this blog, we’ll explore various medications for fibromyalgia, shedding light on their mechanisms, potential benefits, and considerations for those seeking relief.
1. Pain Relievers:
One of the primary symptoms of fibromyalgia is widespread pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can offer some relief. However, prescription medications such as tramadol may be recommended for more severe pain.
2. Antidepressants:
Certain antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are commonly prescribed for fibromyalgia. These medications not only help manage pain but also address sleep disturbances and mood issues associated with the condition.
3. Anti-Seizure Medications:
Medications originally designed to treat seizures, like pregabalin and gabapentin, have been found effective in reducing pain associated with fibromyalgia. They work by calming overactive nerve signals and can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing neuropathic pain.
4. Muscle Relaxants:
Fibromyalgia often involves muscle stiffness and tension. Muscle relaxants like cyclobenzaprine may be prescribed to help ease these symptoms, promoting better flexibility and reducing discomfort.
5. Sleep Medications:
Sleep disturbances are a common challenge for individuals with fibromyalgia. Medications such as certain muscle relaxants, sedatives, or low-dose tricyclic antidepressants may be prescribed to improve sleep quality.
6. NMDA Receptor Antagonists:
Medications like memantine, originally developed for Alzheimer’s disease, have shown promise in managing fibromyalgia symptoms. By modulating the activity of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, they may help reduce pain sensitivity.
7. Topical Analgesics:
For localized pain, topical treatments such as creams, patches, or gels containing analgesic compounds like lidocaine or NSAIDs can be applied directly to the affected areas, providing targeted relief.
Conclusion:
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of medications can vary from person to person, and finding the right combination may involve a process of trial and error. Additionally, medications should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include lifestyle changes, exercise, and alternative therapies. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or discontinuing any medications for fibromyalgia, as they can provide personalized advice based on individual needs and health conditions. Remember, managing fibromyalgia is a collaborative effort, and finding the right balance can significantly improve the quality of life for those navigating the challenges of this complex condition.