Over the past decade, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology that is revolutionizing various industries worldwide. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing involves creating objects layer by layer based on digital 3D models. This innovative technology provides unmatched capabilities in terms of customization, complexity, speed, and sustainability. As 3D printing continues to evolve and become more accessible, it is bringing about breakthroughs across diverse sectors.
Healthcare
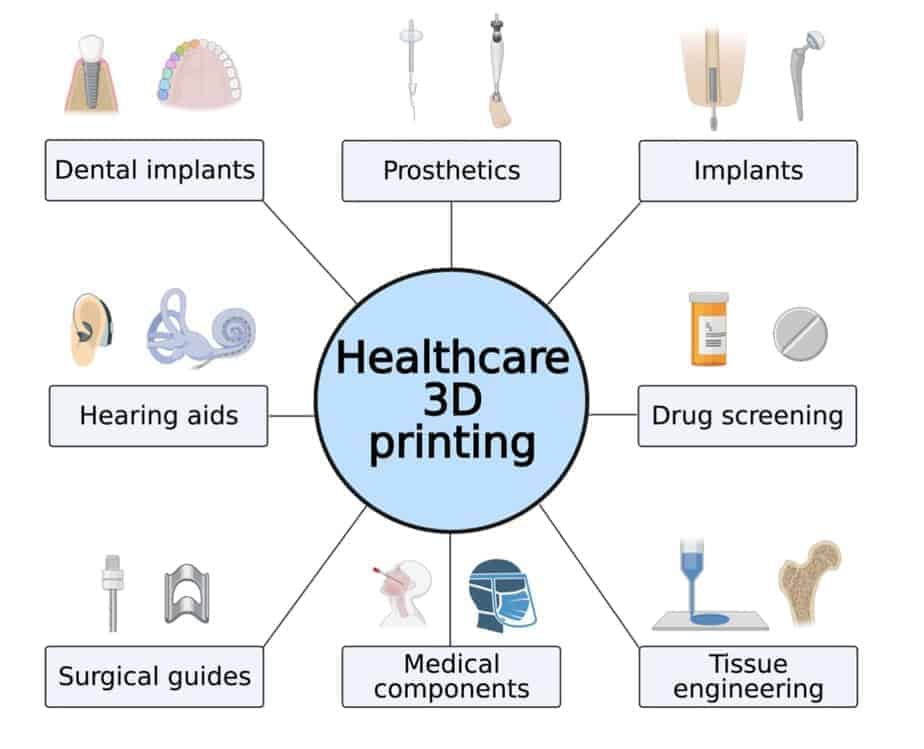
The healthcare industry is harnessing 3D printing to provide better patient care through customization and enhanced precision. 3D printing is being used to create customized prosthetics, implants, and anatomical models for surgical planning and medical training. One significant application is in prosthetics – 3D printed prosthetic limbs can be custom-fit to a patient’s body in terms of size, shape, and weight. This improves comfort and mobility. 3D printing also allows doctors to print customized implants, like hip implants, precisely matched to a patient’s anatomy.
Moreover, complex anatomical models of patient organs can be 3D printed prior to surgery. This enables surgeons to visualize and plan complex procedures on an accurate 3D replica, leading to improved outcomes. 3D printing of tissues and organs is also being researched, which could provide solutions to organ shortage in the future. Overall, 3D printing is enhancing healthcare by facilitating customization, boosting surgical accuracy, and enabling research.
Automotive
The automotive industry has integrated 3D printing to streamline design and manufacturing. Complex parts, like air ducts and cylinder heads, can be 3D printed faster and cheaper compared to conventional techniques. This also reduces material waste. Mechanically functional components can be 3D printed in one part, replacing assemblies. This reduces the number of sub-components, inventory, and tooling costs. Customized and on-demand automotive parts can be quickly 3D printed based on specific customer requirements.
3D printing also enables quick prototyping of vehicle parts during design and testing. New designs can be swiftly prototyped, tested, and modified, accelerating the overall vehicle development process. Lightweighting of vehicles is being achieved by 3D printing optimized and topologically optimized auto parts. Overall, automakers are leveraging 3D printing for greater design flexibility, shorter lead times, leaner supply chains, and lightweighting.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry has been an early adopter of 3D printing for aircraft components. Lightweight aerospace parts with complex geometries, like airfoil shapes, can be 3D printed. This reduces aircraft weight and fuel consumption. Engine parts, like nozzles, can be 3D printed with better heat resistance and durability than conventional manufacturing. 3D printing also enables parts consolidation, reducing assembly requirements. Boeing and Airbus are using 3D printed components on commercial planes like 787 Dreamliner and A350XWB.
SpaceX has 3D printed the main engines of its Falcon 9 rockets using superalloys. NASA is advancing 3D printed rocket engines to power future crewed space missions. Maintenance and availability of spare parts is being improved by on-demand 3D printing of parts during space missions. Overall, aerospace companies are driving innovation via 3D printed parts with superior properties and performance.
Construction
From houses to bridges, 3D printing is steering innovation in the construction industry. Additive construction enables free-form fabrication of buildings as per architectural designs, without the constraints of traditional techniques. Complex 3D printed concrete structures are being built faster, cheaper, and with less wastage. On-site 3D printing robots can construct houses and relief shelters on location, reducing logistics costs of transporting parts.
Countries like China have 3D printed small villages and plan to 3D print a 500,000 square meters smart city. 3D printing allows constructing highly detailed architectural models for design visualization. Companies like Winsun and Apis Cor are building affordable 3D printed homes. Overall, 3D printing is enabling next-gen customized construction with enhanced design freedom, sustainability and speed.
Education
3D printing is transforming STEAM education with hands-on learning opportunities. Students can 3D print and interact with models of molecules, cells, organs, historical artifacts, geometrical shapes and mathematical graphs. This makes learning highly interactive and engaging. Educators are integrating 3D printing into curriculums for science, technology, engineering, arts and mathematics.
Students are also learning creative problem-solving, design thinking and digital fabrication skills by designing their own 3D printed objects. 3D printing fosters project-based and experiential learning. Educational institutions have setup fab labs with 3D printers for students to learn and innovate. 3D printing enables tactile learning aids for visually-impaired students. Overall, 3D printing is making education experiential and inclusive.
Fashion
3D printing is empowering greater customization, sustainability and supply chain flexibility in the fashion industry. Designers are 3D printing custom-fit garments based on customers’ exact body measurements. This addresses the problem of mass-produced clothes fitting imperfectly. Small batch manufacturing of 3D printed fashion accessories and footwear is also gaining traction. Companies like Adidas and New Balance are 3D printing athletic shoes.
Fabric waste is reduced by additive manufacturing of garments and fabrics. Sustainable materials like orange peel waste and recycled plastics are being used for 3D printed clothes. On-demand localized production enables compressing supply chains. Overall, 3D printing is enabling startups and brands to provide customized fashion sustainably and efficiently.
Food
The $8 trillion global food sector is leveraging 3D printing for innovative food design and nutrition. Intricate chocolate shapes, pasta, and pizza bases can be 3D printed. Personalized nutrition is being enabled by food companies like Natural Machines with 3D printers for home use. Nutrient levels in 3D printed foods can be customized based on consumers’ health profiles. 3D printing also makes cooking easier. 3D food printers for restaurants and commercial kitchens enable cooking with ingredient cartridges at the push of a button. This reduces labor and expands menu options. Meat companies are also exploring 3D printed meat alternatives to develop sustainable food options.
Conclusion
As evident, 3D printing is revolutionizing industries in groundbreaking ways. While the technology has been around for decades, recent advancements are enabling greater capabilities and mainstream adoption. As 3D printers become faster, cheaper and able to print a wider range of materials, the applications will exponentially grow. 3D printing is creating opportunities for distributed and customizable manufacturing, resulting in supply chain innovations. It empowers businesses and consumers to be producers as well as customers. While the technology has its limitations currently, it is improving rapidly. In the coming decades, 3D printing promises to transform how we design, produce and distribute almost everything, unleashing the next industrial revolution.







![Top CEOs under 30-The Young Guns Of Technology [Infographic]](https://lerablog.org/wp-content/plugins/wp-thumbie/timthumb.php?src=http://lerablog.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/the-young-guns-of-technology.jpg&w=300&h=140&zc=1)


