Database as a Service (DBaaS) providers provide databases and their infrastructure in the cloud. This model reduces IT costs, freeing up staff and resources to focus on applications and extracting value from data.
It also provides greater flexibility and control over the database. Additionally, DBaaS providers offer security features such as encryption-at-rest, which protects data from theft and other threats.
Cost-effectiveness
Database as a service allows users to scale their databases on demand without purchasing and installing hardware. Users can quickly add storage and computing capacity to meet high processing demands, such as end-of-quarter reporting or seasonal spikes in e-shopping. Moreover, they can quickly scale down during non-peak usage. This elasticity helps to keep costs low while increasing the availability of data records.
Additionally, DBaaS providers take care of most maintenance tasks. This includes installing security patches, monitoring performance, and providing backup and recovery services. This can help save time and money for the business and reduce the risk of disruptions and downtime.
In addition, the DBaaS model has maximum high availability and eliminates a single point of failure. The platform can automatically reroute traffic to a standby database instance and ensure the data is available even during a server crash. This is especially important for mission-critical applications that require zero downtime.
In addition, DBaaS makes it easier for developers to work with data. By removing the burden of infrastructure management, they can focus on building and extracting valuable insights. As a result, they can drive innovation and improve business outcomes. However, it’s essential to understand your organization’s critical drivers for DBaaS adoption. Some common reasons include cost reduction, improved flexibility, and digital transformation initiatives.
Security
When choosing a database as a service, look for providers that follow security best practices. These include a firewall that prevents direct connections to the database and only allows traffic through with authorization and audit trails. In addition, a database as a service provider should have an in-depth knowledge of how to protect databases against data breaches and other vulnerabilities.
Unlike an in-house database setup, DBaaS does not require expensive hardware or software installation and provides scalability on demand. It also eliminates time-consuming tasks and gives teams agility for faster software development. It also helps reduce IT spending by removing hardware and staffing requirements and enabling organizations to pay for what they use.
Security measures that a database as a service provides can include database-specific firewalls, specialized tools to manage access and privileges, and database-specific passwords. These tools can help prevent unauthorized access to the database and provide more effective data control. Implementing a solid network and application access management policy that follows the principle of least privilege and grants access only for a limited period is essential.
Database as a service (DBaaS) is a cloud computing service that lets users store and manipulate databases without needing physical infrastructure or maintenance. It uses a web-based interface or API endpoints to enable access and management of databases. It supports relational and non-relational database technologies, including open-source options.
Scalability
Databases are essential for the operation of most businesses, whether they’re hosting email servers, customer data, or extensive data archives. They need to scale up and down to handle spikes in demand quickly. DBaaS is an excellent solution for this, and it also saves the business money by reducing hardware costs. But not all DBaaS providers are the same. They were choosing the right one for your business and a provider that meets the technical requirements of your application workloads.
DBaaS providers often offer multiple databases, which users can access via web-based interfaces or APIs. These interfaces allow developers to monitor and control database performance. They can also perform tasks like adding, deleting, and updating data. The scalability of DBaaS also reduces operational costs by eliminating the need for in-house hardware and personnel.
DBaaS can add agility, flexibility, and scalability to development teams, no matter the size or industry of their business. By freeing developers from maintenance duties, they can focus on delivering value to customers and increasing business growth. Moreover, DBaaS can save companies from hiring a full-time IT team to manage their database infrastructure and ensure that it’s running at optimal performance. This can significantly cut operating expenses and free up valuable human resources. In addition, DBaaS provides rapid provisioning capabilities and self-service options for users, which reduces the governance hurdles and administrative responsibilities that IT departments typically face.
Flexibility
DBaaS provides flexibility for data operations and reduces costs. It also simplifies development and deployment forenterprise developers. The DBaaS model ensures high availability and eliminates a single point of failure. If there is a problem with a database instance, the system automatically reroutes database connections to a standby instance. This reduces downtime and prevents loss of data.
The DBaaS model also provides scalability so users can add more storage and processing capacity for peak loads. This flexibility is essential for enterprises that experience seasonal spikes in e-shopping and other business processes. Moreover, DBaaS offers on-demand pricing, so users pay only for what they use.
Small businesses can benefit from a DBaaS provider by saving on hardware and personnel costs. Instead of hiring an entire IT department to manage databases, they can focus on growing their business. DBaaS providers handle infrastructure management, database administration, and software updates. However, they may have limitations and restrictions on configurations and hardware choices. They also need help offering the same data security level that a company would have in-house. Additionally, if the DBaaS provider’s data center is located far from the user’s location, there could be increased loading times.


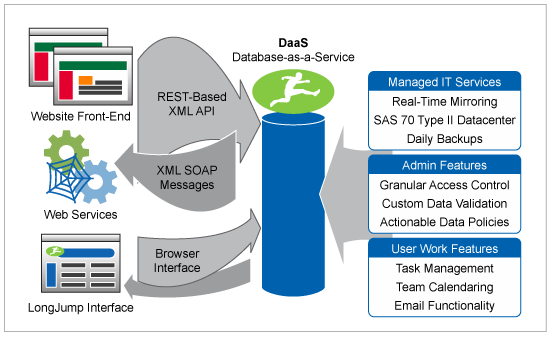







This article provides an excellent overview of the advantages of Database as a Service (DBaaS), shedding light on its cost-effectiveness, scalability, security, and flexibility. It’s a valuable resource for businesses aiming to optimize their data management processes.
However, I have a question regarding the selection of a suitable DBaaS provider. With so many options available, how can businesses ensure they choose the right provider that aligns with their specific technical requirements and application workloads? Any guidance on this aspect would be greatly appreciated.