Chronic inflammation is a long-lasting inflammatory condition that persists because of aggressive stimuli. Inflammation itself is actually a positive thing, as it’s the body’s self-protection response. Its intended purpose is to ‘burn out’ the cause of the problem, like bacteria or virus. In injuries, inflammation speeds up natural tissue repair and actually prevents necrosis. Therefore, inflammatory reactions aren’t bad by default, but they definitely become dangerous if they persist. Chronic inflammation greatly lowers the quality of life and increases the risk of numerous diseases, including cancer, stroke, and heart disease. Its treatment is a gradual process that requires multiple dietary and lifestyle changes.
Chronic inflammation is a long-lasting inflammatory condition that persists because of aggressive stimuli. Inflammation itself is actually a positive thing, as it’s the body’s self-protection response. Its intended purpose is to ‘burn out’ the cause of the problem, like bacteria or virus. In injuries, inflammation speeds up natural tissue repair and actually prevents necrosis. Therefore, inflammatory reactions aren’t bad by default, but they definitely become dangerous if they persist. Chronic inflammation greatly lowers the quality of life and increases the risk of numerous diseases, including cancer, stroke, and heart disease. Its treatment is a gradual process that requires multiple dietary and lifestyle changes.
How to Say If You Have Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can occur in two cases:
- The cause of acute inflammation isn’t removed completely
- You’ve contracted a pathogen that causes chronic inflammation by default
Please note that scientists are yet unable to identify the second case and its causes. However, the University of Washington’s courses state it exists.
Symptoms of chronic inflammation are so common that this condition is nearly impossible to diagnose. A blood test is your best bet as it should show an elevated amount of lymphocytes. These are white blood cells, which production increases in response to inflammation. Note that the levels will be much lower than in case of an acute inflammation.
Most common symptoms of chronic inflammation include:
- High levels of blood glucose
- Regular digestive issues (diarrhea, gas, etc.)
- Fatigue
- Skin issues (acne, psoriasis, eczema, etc.)
- Frequent allergies
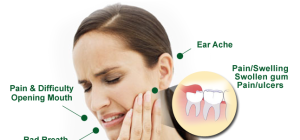
Note that some types of chronic inflammation are easier to identify because they ‘show up’ on a specific area of the body. For example, bleeding, swollen, or puffy gums indicate you have a chronic gum disease, which is a type of chronic inflammation.
Puffy eyelids or crusts on the roots of eyelashes indicate blepharitis (eyelid inflammation). Note that info on blepharitis states that it usually starts as an acute inflammation. However, it’s almost never diagnosed at early stages, so it’s usually chronic by the time you learn why your eyes are so red, dry, and aching.
As chronic inflammation can be extremely dangerous, due to it weakening your body on a daily basis, it’s essential to ‘catch’ it as fast as possible. Be sure to consult with your doctor and take a blood test if you are feeling ‘under the weather’ for no reason.
Chronic Inflammation Treatment and Management
To cure chronic inflammation, one needs to solve the problem, which causes it. In some cases, like with autoimmune diseases, the underlying condition might be incurable. Therefore, chronic inflammation treatment and management usually go hand in hand. Patients are prescribed various anti-inflammatory agents to reduce the condition as much as possible. After that, diet and lifestyle changes become the key to keeping it at bay.
The most efficient chronic inflammation management practices are:
- Regular mild-to-moderate workouts.
A 10-year long study indicates that people, who exercise at least 2.5 hours a week have 12% lower inflammatory markers. Note that strenuous training, like the practices of professional athletes or bodybuilders, have an opposite effect. - Maintaining a healthy sleep schedule.
UCLA researchers proved that even a few missed hours of sleep trigger inflammation in the body. This means that not only do late nights contribute to chronic inflammation, they can cause it. Keeping to a healthy sleep schedule is difficult, especially if you suffer from insomnia, anxiety, or depression. Funnily enough, those might all be caused by the lack of sleep. The best practices for dealing with this problem are mastering mindfulness meditation and relaxing herbal teas. You can also try some yoga, but skip out on sleep aid drugs as those trigger inflammation all on their own. - Keep a healthy anti-inflammatory diet.
Diet for chronic inflammation management must contain more fiber (no less than 25g a day) and omega 3 fatty acids. The latter are most important as they are natural anti-inflammatory agents. You can get them from fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseed. It’s also essential to reduce your intake of omega 6 fats to the barest minimum (no plant cooking oils, fat meat and dairy). You’ll also have to exclude all processed foods and replace junk foods with healthy snacks, like nuts or dried fruits (without sugary syrup). Eating no less than 10 servings of fruits and veggies a day is also greatly encouraged.
Living with chronic inflammation isn’t easy, but managing the condition is possible with some lifestyle changes. Note that you’ll have to learn how to observe your body and seek medical help whenever you feel it weakening.