 Rapid Application Development is a strategy to get feedback from users as quickly as possible and implement changes after each iteration. Find out about RAD and find out if it’s something you would like to use for your project.
Rapid Application Development is a strategy to get feedback from users as quickly as possible and implement changes after each iteration. Find out about RAD and find out if it’s something you would like to use for your project.
RAD or Rapid Application Development is an approach that focuses on designing and prototyping stages with the intention of getting immediate user feedback. Unlike traditional development, RAD’s initial planning and execution mean more flexibility. The constant repetition of user feedback and fast incremental updates will help to achieve greater results by the end of the day.
James Martin said it best when talking about rapid application development in 1991. It’s an alternative to the rigid waterfall processes. The classic waterfall approach works perfectly in construction and many other industries where changes are rare and expensive. If you started building a bridge, it is unlikely you would swap it for something else halfway through the project.
Phases of Rapid Application Development Methodology
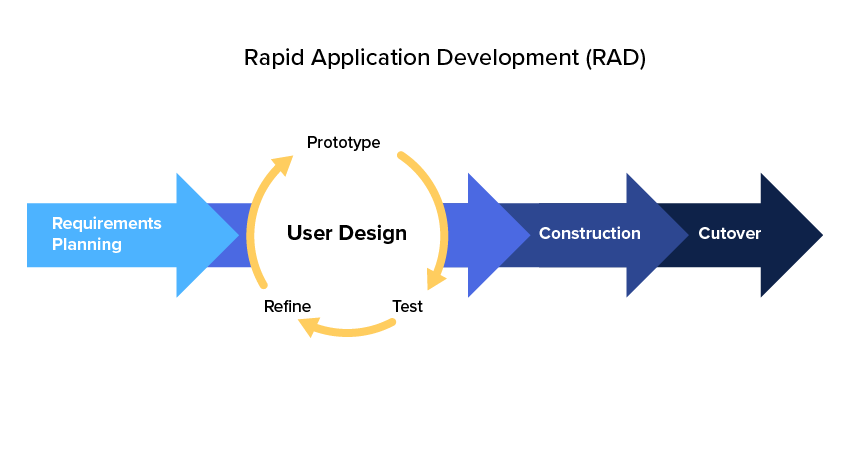
RAD shifts focus from costly planning to prototyping. In particular, RAD suggests the process is divided into four stages:
The Planning Requirements
During this phase, users and the project team will identify the objectives of the future system. The focus should be on reaching a business goal and the requirements are vague. Being able to adjust or change them during the prototyping stage is important.
User Design
User design is a critical part of the rapid application development stage distinguishing it from the classic waterfall design. From this point, developers will start by working on a prototype. The goal is to demonstrate it to the client as soon as possible and as cheaply as possible. It is acceptable for the prototype to satisfy part of the requirements or cover only certain scenarios. At the code level, it’s acceptable to cut corners.
Once the prototype is ready, it is presented to the users. The team will collect all possible feedback and that’s when the initial requirements are subject to inevitable changes. If something might seem right on paper but could be completely different in a working application. With feedback in hand, developers will return to the prototyping stage until the users are satisfied with the end result.
During Construction
At this stage, everyone knows exactly what must be done. It’s time to develop and test the system in order to be ready for production. There are no cutting corners, the focus will be on quality, scalability, maintainability, etc. While users will continue to take part, even at this stage, by providing feedback as features are being included. During this stage, fine-tuning is possible for the rapid application development cycle.
What has been developed at this stage might even get thrown out, depending on the tools chosen and other circumstances for rapid application development.
Cutover
This is the final phase including acceptance training, rollout, and user training.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Rapid Application Development
Rapid application development swings the balance from predictability to agility with several pros and cons.
Advantages
Higher Quality
With users deeply engaged in the prototype stage, the outcome of the software will probably be more relevant for their work and will match their expectations
There Will Be Fewer Costs and Risks
Using the waterfall path, users will only see the results and provide feedback when the project is delivered. The inevitable changes at this stage are expensive and very time-consuming. With rapid application development methodology, the risk of re-writing half of the solution after it is rolled out will be minor.
Disadvantages
The Lack of Scalability
The RAD assumes very close collaboration took place between the team and end-users. When the team becomes too big, or there are too many stakeholders, the prototyping process will slow down significantly. It will become more difficult to communicate frequent scope changes between everyone involved. RAD is considered favorable for small or medium-sized teams.
Poor Design
Chasing down specific business features and cutting corners at the prototyping stage can lead to a poor overall solution design.
Lack of Control
For obvious reasons, it’s impossible to plan objectives, requirements, budget, and time until the project is out of the prototyping stage. That said, basic expectations can be set based on the results of the requirements planning phase.
End-Users Commitment
Rapid application development believes the deep involvement of users during all stages of the project is required. This is especially true for the most knowledgeable people in the business who are usually the busiest people in the company.
Rapid Application Development or Agile?
The term RAD was before Agile by 10 years and due to its repetitive approach it’s considered the forerunner of Agile. While rapid application development is a prescriptive development, Agile is a philosophical position encompassing much more than development.
It’s fair to say that RAD is in the family of Agile software development methodologies along with Scrum, Kanban, and many others.
Is Rapid Application Development applicable to my project?
As discussed earlier on, RAD does not work in stringent environments. It’s not applicable when:
- The budget and timeframe must be known in advance
- You will not have regular access to the users or if they are not motivated to commit their time and energy
- The project requires a large team due to its scale or there is an excessive amount of stakeholders.
These requirements are true for large businesses or governmental organizations. That said, there are certain elements of rapid application development methodology that can be applied even in such cases including fixed-price projects that can budget for prototype stages and a certain amount of changes. Prototype scope could be limited to the most uncertain factors if you have relevant users on board.
On the other hand, a rapid application development framework is good for small and medium businesses or departmental projects where business users own the budget and are motivated to get results. A good example is Line-of-Business applications. LOB is a general term for applications developed to automate and run specific parts of a business more efficiently.
RAD is a perfect application for creating websites. They are usually small projects with limited stakeholders but involving them early on is important as design is an opinionated aspect and everyone will have something to say.
Rapid Application Development Tools
The success of RAD methodology depends on prototyping speed and close collaboration and choosing the right tools for support is extremely important.
Design And Prototyping
Rapid application development tools and InVision enables graphic designers and UX specialists to quickly knock out and share with end-users clickable prototypes with a total design to get feedback. Once the emphasis of the prototype is approved, the project can be sent to formats that are reusable by front-end developers and then move into the construction phase. These tools are widely used for creating websites but also for the prototyping user experience of more complex end-user applications or portals.
Other tools such as Balsamiq are more commonly used by business analysts focused on prototyping user experience with wireframes while the final design can be applied later on. These are good choices for the basic shaping of larger systems with complex user interaction.
Development
Without a doubt, development is the most time-consuming, expensive, and uncertain aspect of creating an application. The modern rapid application development platforms bring together proven architecture, and ready components, using typical features, and tools assisting the progress of rapid development. All of these will help deliver the results needed more quickly for both the Prototyping phase of the project and further on during Construction. Many consulting firms keep introducing new terminology to distinguish between these platforms:
LCAP – Low/No Code Application Platforms, HPAPaaS – High Productivity Application Platforms as a Service, MXDP – Multi Experience Development Platforms.
Low Code, No Code Platforms
The idea of working with these platforms is to allow business users with no development skills to provide working applications quickly. This means a lack of flexibility and many limitations. As a result, the niche of these platforms is prototyping or just basic systems.
Developer Focused Platforms
These platforms weigh the speed and satisfaction of software development by providing higher-level API and code generation in order for developers to be kept away from repeating boilerplate code and typical functionality. Borland Delphi is a pioneer in this field and known for its visual UI design. It seems before the web era, it was still applicable for desktop and mobile applications.
There are other application development frameworks that focus on the web because it’s a powerful channel for interaction with end-users. Using the Jmix rapid application development platform you can join the convenience and speed of visual data and interface design with modern open source technologies. This approach not only boosts prototyping speed but enables you to grow your prototype into a full-featured enterprise application with solid and scalable architecture.
Conclusion
Rapid Application Development is one of the development methodologies that follows the agile philosophy. The principle behind RAD is a close engagement of end-users and fast, repetitive prototyping based on user feedback.
Choosing the right tools is important to ensure fast prototyping and successful implementation of RAD methodology in a project. There is a wide choice of tools and platforms aimed at different types of applications, stages of a project, and team skills. RAD is an old concept but today it’s experiencing a renaissance following the trends of digital transformation and a push toward faster time to market. With the right types of projects and team setup, the RAD methodology will help to achieve better user satisfaction with reduced risks and shorter timeframes.







