Have you ever felt like you just can’t hold it in? If your answer is yes, then you’re not alone. You may be the victim of Urinary Incontinence, which is very common and effects people ranging from kids to adults. Yes, it can be embarrassing, but the more you know about it, the better prepared you are to deal with it. So let’s just start unfolding the mystery behind the incontinence.
Have you ever felt like you just can’t hold it in? If your answer is yes, then you’re not alone. You may be the victim of Urinary Incontinence, which is very common and effects people ranging from kids to adults. Yes, it can be embarrassing, but the more you know about it, the better prepared you are to deal with it. So let’s just start unfolding the mystery behind the incontinence.
What is Urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence (UI) is the involuntary leakage of urine. In layman terms UI is the inability of the bladder to hold urine, means to pee when you don’t intend to.
Who can be affected with UI?
It can affect both men and women of any age group, but it is found to be more prevalent in women and the elderly. And, although the rate is much lower for younger adults, it can still be quite common. Stats suggest that around 200 million people around the globe are suffering from the problem of urinary incontinence.
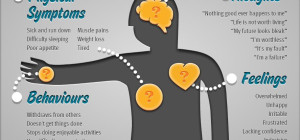
Symptoms of UI:
- Involuntary release of urine triggered by your coughing, sneezing or laughing.
- A sudden uncontrollable urge to urinate.
- Leaking of a moderate to small amount of urine frequently.
- Difficulty in initiating urine.
- Decrease urinary stream.
Causes of temporary incontinence:
Certain foods, drinks and habits can result in the problem of incontinence.
- Alcohol: An urgent need to urinate can be caused by the diuretic nature of alcohol.
- Over hydration: Increase in intake of a lot of fluids in a short period of time can increase the amount of urine your bladder has to deal with.
- Caffeine: Like alcohol caffeine also comes under the diuretic categories which can triggers an urgent need to urinate.
- Bladder Irritation: Foods and beverages which are high in spice, sugar and acid can aggravate the bladder.
- Medications: Blood pressure drugs, sedatives and medications may contribute to bladder control problems.
- Urinary tract infection: Irritation of bladder due to urinary infections can result in incontinence.
- Constipation: Due to the location of the bladder in vicinity to the rectum sometimes constipation can lead to increase in urinary frequency.
Causes of persistent incontinence:
- Pregnancy and childbirth: Hormonal changes, increased weight of an enlarging uterus and a vaginal delivery can weaken muscles needed for bladder control.
- Changes with aging: Aging of the bladder muscle contributes to the decrease in the urine storing capacity of the bladder.
- Hysterectomy: Surgery involving women’s reproductive system may sometime leads to damaging of the supporting pelvic muscles ultimately leading to incontinence.
- Enlarged prostate: Older men can offer suffer incontinence due to enlargement of their prostate gland.
- Prostate cancer: Untreated prostate cancer or the after effects of the surgery, radiations of cancer can lead to the problem of incontinence.
- Obstructions: A tumor anywhere along the urinary tract can block the urinary flow and may result in overflow incontinence.
- Neurological disorders: Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer, brain tumor or a spinal injury can create interference in nerve signals and can result in incontinence.
Types of urinary incontinence:
- Stress incontinence: Most common type of incontinence, especially among women. Stress here refers to physical pressure and not mental stress. An extra pressure on bladder and muscles involved in urinary bladder can lead to involuntary release of urine.
- Urge incontinence: Here the bladder is either unstable or overactive. Involuntary contraction of the muscular wall of the bladder suddenly can causes urinary urgency. It can happen during sleep, drinking water, or when you hear or touch running water.
- Functional incontinence: People having problems in thinking, moving or speaking that keep them from reaching the bathroom may suffer with this type of incontinence.
- Overflow incontinence: This occurs because the bladder doesn’t empty completely. Here the patients frequently dribble urine. It is common in enlarged prostate patients.
- Mixed incontinence: When stress and urge incontinence occur together, they are known as mixed incontinence.
Social and mental effects of UI:
Urinary incontinence treatment is needed as the problem can have an impact on the physical, psychological and social well-being of the patients. Depression and incontinence both results in decrease in quality of life. When they occur together they have a combined effect on the mental and physical health leading to a negative perception of the person towards their illness. Embarrassed of their problem the sufferers never come up with it and end up being isolated.
Facts that you need to know:
- Nearly thirteen million American people are affected by urinary incontinence, among which 85 % are women.
- Stats show that every fourth women over the age of eighteen experience involuntary urinary leaking at some interval of her life, and every fifth adult over forty have recurring urinary urgency and frequency.
- Ten percent of children over five years have problems with bed-wetting, and 1% of them continue to have this problem till the age of sixteen.
- Urinary incontinence is reported by fifteen to forty percent of women over sixty.
- Complains of urinary incontinence has been reported more than 50 percent of women in nursing homes.
- Prolapsed (sagging) of the vagina, uterus, urethra, small intestine, or rectum have been found in nearly 50 percent of the women who have had children.
- Elder women are 2 times more likely to suffer from urinary incontinence than men.
Is urinary incontinence curable?
The answer is “YES”. Of course incontinence is curable and can be treated. Treatment depends on type of urinary incontinence, its severity and the underlying cause. Some of the treatments are:
- Behavioral technique: This technique is associated with change in the habits and lifestyle. Methods like Bladder training, Scheduled toilet trips and Fluid & diet management are associated with this technique.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening and tightening of the bladder muscles are the ultimate goal of this technique. Methods like Pelvic floor muscle exercise and Electrical stimulation are associated with this technique.
- Medications: Behavioral methods are often accompanied with medications. Drugs used to treat incontinence are Anticholinergics, Topical estrogen etc.
- Medical devices: Several medical devices like Urethral insert and Pessary are available to help treat incontinence.
- Surgery: If other treatments don’t work properly then surgery could be a fine option to fix the problem of incontinence. Some of the techniques are Sling procedure, Bladder neck suspension, etc.
- Absorbent pads and catheters: If medical treatments failed to eliminate your problem completely or you need help until a treatment starts to take effect than you can try incontinence products like pads & protective garments and catheters that help ease the discomfort and inconvenience of leaking urine.
Remember, if you suffer from incontinence, you are not alone! It is an easily solvable and common problem that you don’t need to feel ashamed of. With the help of proper treatment and disciplined lifestyle you can overcome this. Don’t let this problem to drag you into depression or embarrassment. All you need to do is to show some courage and fighting spirit and believe yourself and rest all will be fine.