The birth control pill is the most commonly used method of contraceptive medicine being used by nearly 67% of all women who use contraceptives to avoid pregnancy. Despite the known side effects that are accompanied by taking these pills, many women still prefer using this method as compared to all the other available methods of contraceptives.
As the majority of women take this pill to primarily avoid accidental pregnancies, some take it with the intention of either stopping or regulating their menstrual cycle. Sometimes they are used to reduce symptoms of hormonal imbalance. These hormonal imbalance symptoms include experiencing painful cramps during menstruation, acne and heavy bleeding.
Birth control pills are considered to be both efficient and effective as studies have shown them to be 99% effective when used correctly. On the other hand, other people feel that the well-being of their physical and mental health which might be altered by using the birth control pill far outweigh the benefit of pregnancy prevention.
These critics suggest that women should consider other safer forms of pregnancy prevention such as abstinence from sexual intercourse or use of condoms. When considering taking birth control pills as a method of contraceptive one is advised to fully know and understand the probable side effects she might encounter in her day-to-day life. Birth control pills contain hormones that not only prevent pregnancy but are also responsible for other body functions.
When using these pills, the hormones included may change some aspects of the body. These changes are categorized as either positive or negative depending on an individual. Most of the side effects are said to go away in 2-3 months after the day you start taking the pill. Nevertheless, many people who have used the pill admit to not having any problems at all.
Types of Birth Control Pills
There are many brands of birth control pills from different companies around the world but all of them fall under two categories: progestin-only pill, and combined pill.
Progestin-Only Pill
These are contraceptive pills that only contain progestin hormone and are commonly prescribed to women who have a history of drug interaction after using a combined pill. These birth control pills work by causing the mucus on the cervix to thicken and thin the lining of the uterus rather than stopping ovulation. There are lesser brands of progestin-only birth control pills as compared to the combined pill due to their tendency to cause breakthrough bleeding.
Combined Pill
This birth control pill contains more than one synthetic female hormone. These synthetic hormones mimic the progestin and estrogen effect of stopping ovulation to prevent pregnancy. This combination of the two hormones also stops fertilization of the egg by thinning the uterus lining and making the cervical mucus to thicken.
These pills are to be taken in a cycle of 21-24 active days every month and about 7 days off without taking the pill. Even in the 7 off-days, the woman will still be able to avoid pregnancy. There are some combined birth control pills that contain a lower dosage of estrogen hormone and are usually recommended to women who are sensitive to high estrogen levels.
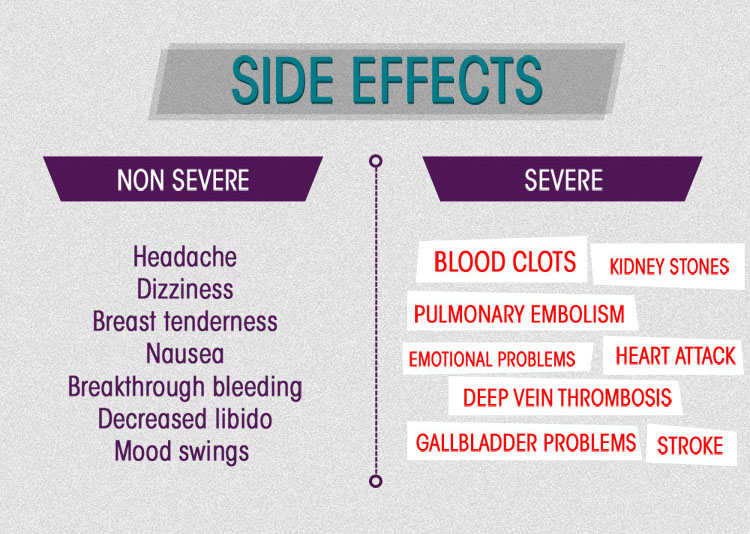
The 10 Most Common Birth Control Pill Side Effects
Birth control pills are known to unnaturally raise the estrogen hormone levels in the female body. A normal menstrual cycle records fluctuating level of progestin and estrogen hormones all through the month. These birth control pills work by maintaining a high level of estrogen hormone throughout the month. A high level of estrogen fools the body to think that it is already pregnant and it sends a signal to stop the ovulation.
Studies have shown that continuous use of birth control pills may have the following side effects that are as a result of increased level of the estrogen hormone continually.
- Nausea: some people report to having experienced nausea but it should disappear within a few days usually, less than three months from the start day.
- Irregular menstrual bleeding: intermenstrual spotting is common in between periods but resolves within 3 months. The pill still maintains its effectiveness even during spotting as long as it’s still taken correctly and without absconding. If a woman experiences five or more days of heavy uterine bleeding when using the pill, she should consult a doctor. This type of bleeding is usually a result of the uterus adjusting to the thinning of the endometrial lining or just adjusting to the new environment of high hormone levels.
- Breast enlargement: the breasts may feel more tender and larger than normal. This will resolve itself a few weeks after starting the pill. If a woman identifies a lump formation in the breast or continually experiences persistent pain, she is advised to consult a doctor. Wearing a supportive bra can help relieve the feeling of breast tenderness. Reducing or avoiding salt and caffeine intake is also effective in relieving the tenderness.
- Extra weight: although there has never been a direct link between the use of birth control pills and weight gain it has been proven that use of the pill may promote fluid retention especially in the breasts and hips.
- Headache and migraines: progestin and estrogen hormones are known to increase the chances of experiencing headaches and migraines. Changing to a birth control pill of lower dosage might help resolve this problem.
- Changes in mood: scientists have established a link between mood changes and the use of birth control pills. It can trigger depression and other emotional changes.
- Receiving less or no periods: this is one unavoidable side-effect of the birth control pill even when it is used correctly. Other factors such as stress, illnesses, and hormonal abnormalities may influence the normal menstrual cycle. If a woman misses her periods consistently she is advised to take a pregnancy test before starting the next pack of pills.
- Libido decrease: the hormones in a birth control pill are known to alter a woman’s sex drive. In some cases, they can increase the libido.
- Discharge from the vagina: when taking the pill vaginal discharge might be noticed due to the increase or decrease in normal vaginal lubrication. Low vaginal lubrication can be solved by the use of artificial lubricants to make intercourse more comfortable.
- Changes in the eye cornea: the hormones in a birth control pill can thicken the cornea of the eye as well as increase the chances of getting an eye disease.
Contributed byhttps://www.obgynqueensnyc.com/